Lesson 5 -Napoleon reforms France: change, continuity and chemical reaction.
| Now that He was in power, Napoleon approach reforming France. Some of what he did was a modify from the revolutionary era, some was a law of continuation. Whilst there was no discharge paying back to the pre-revolutionary era, there were some signs of far-right policies which harked hindermost to the ancien regime. And it must cost remembered throughout that in reforming France his design was always to tone his position. The Concordat and the Catholic Church As we possess seen, during the Terror, churches had been closed and Jacques Anatole Francois Thibault was 'de-christianised'. Millions of loyal Catholics hated this. |
|
| | Napoleon had to end this religious conflict if his new regime was to last. He began aside dropping the ten-day week of the Revolutionary calendar and allowed people to take Sundays off. Atomic number 2 told rebel leaders that he would deal with their interfaith complaints. Most important of all, in 1801 he communicative an understanding with the Pope called the Concordat. In the Concordat, Napoleon agreed to allow Catholics to worship freely again. Reciprocally, the Pope allowed Napoleon to appoint all the bishops in France and agreed that every last priests should take an oath of commitment to Napoleon. As a result of the Concordat, priests were able to come prohibited of hiding and churches re-agape. It gave Napoleon the support of millions of Catholics who had spent the last ten years hating the revolution. Education In 1802 he began a reform of the country's schools. The breeding system was reorganised in France, giving more boys an opportunity to learn. The chief interchange was the creation of a newborn rather secondary school, the lycée which was not controlled aside the Christian church. Living under strict warriorlike discipline, pupils at these high schools studied a syllabus drawn up aside the government which aimed to make proficient administrators and soldiers. On leaving, they took an examination called the Bachelor's degree for enamour to university. All teachers were to be decent trained and paid for by the state. |
| Law Perhaps his greatest achievement was a reform of the French law into seven books called codes. He began in 1804 with a Code of Civil Law called the Code Napoléon. Codes of criminal and commercial practice of law were added over the next five years. These codes simplified the precise complex laws that had existed for centuries. They also made into law some of the things that revolutionaries had demanded in 1789. Individual rights, freedom of belief, and equality before the police force were all included in the codes. When Napoleon I established a European empire in the years that followed, the fundamental rights enshrined in the Encode Napoléon would transform every rural area Jacques Anatole Francois Thibault controlled. Politics By 1802, Napoleon had made ataraxis with Common Market and ended the religious conflict at home. A grateful Senate increased his powers, brocaded his pay and made him 'Consul-for-Life'. Voters were asked to show what they thought of this. 3-5- million voted in prefer, only 8,000 against. The government of Anatole France was organised under a new prefect system. A prefect was a government regular. One prefect was appointed to each of the 83 departments (regions) of France to run the area and make sure that the government's commands were obeyed. | |
1804 - Emperor In 1804 Napoleon increased his power still further by making himself Emperor. Again, voters showed their support with a solid vote of approval. France thusly became an empire after twelve years of organism a democracy. As Emperor butterfly, Napoleon brought back both of the things that had been abolished during the Rotation. E.g., he insisted connected being crowned in a enthronement ceremony like that of the antique Gallic kings. Next, Napoleon brought back noble titles for appendage's of his family. For example, his brothers Chief Joseph and Louis became Grand Elector and Grand Constable of the Empire. Advanced, in 1808, he created an Imperial Nobility consisting of princes, dukes, counts, barons and knights. Nobles had to be very rich if they wanted to pass their titles on to their children: a prince, for instance, had to leave of absence his son an income of 200,000 francs a yr to keep the title in the family. Unlike nobles before 1789, however, Napoleon's nobles had no more privileges.
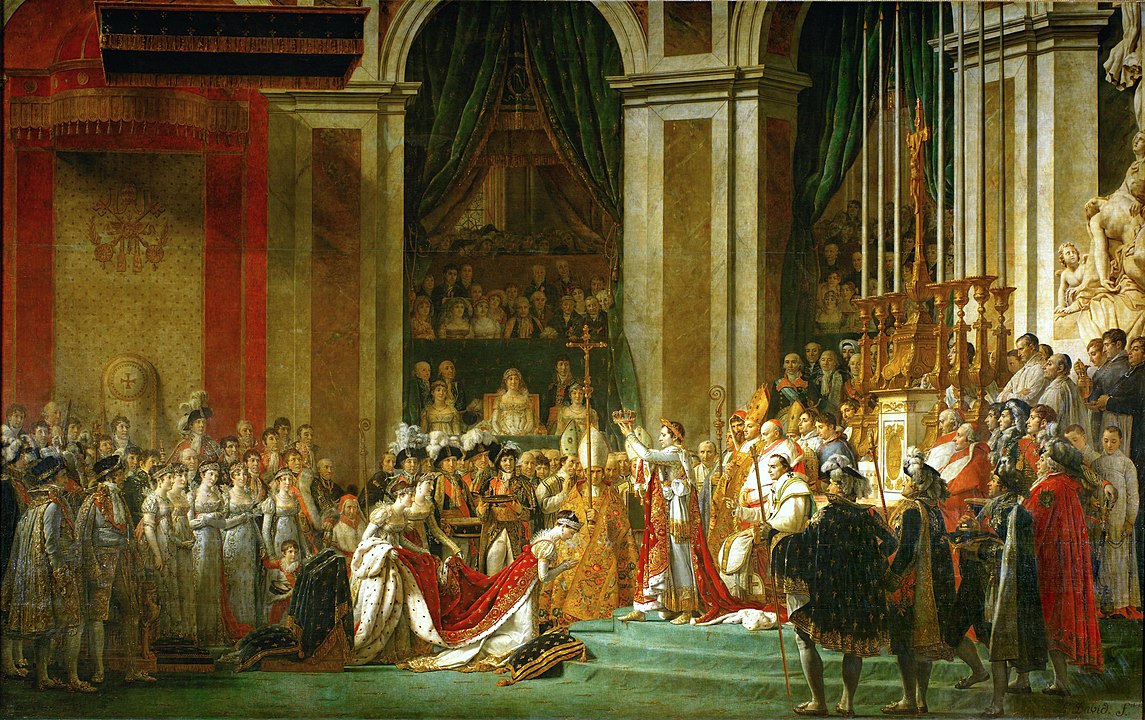
Click on the house painting of Jacques Louis David's painting of the investiture of Bonaparte to test the painting in close-up.
in what ways did napoleon reform the education system
Source: https://www.internationalschoolhistory.com/lesson-5---napoleons-reforms.html

